In today's hyper-connected world, remote access tools are indispensable. They allow IT teams to troubleshoot issues from afar, enable remote work, and keep global operations running smoothly. But flip the coin, and these same tools become one of the most dangerous weapons in a cybercriminal's arsenal.

Welcome to the shadowy realm of Remote Access Tools (RATs) in cybersecurity—where "RAT" can mean a helpful utility or a stealthy Remote Access Trojan.

Legitimate Heroes: The Good Side of Remote Access Tools
Remote access software has revolutionized how we work. Tools like TeamViewer, AnyDesk, Microsoft Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), Splashtop, and ConnectWise ScreenConnect are designed for legitimate purposes:
- Providing technical support
- Accessing files from home
- Managing servers across continents
These tools are secure when used properly—with strong authentication, encryption, and consent-based access.
![AnyDesk vs TeamViewer: In-Depth Feature Comparison [2025]](https://i0.wp.com/blog.islonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/anydesk-vs-teamviewer.jpg?resize=1717%2C1071&ssl=1)
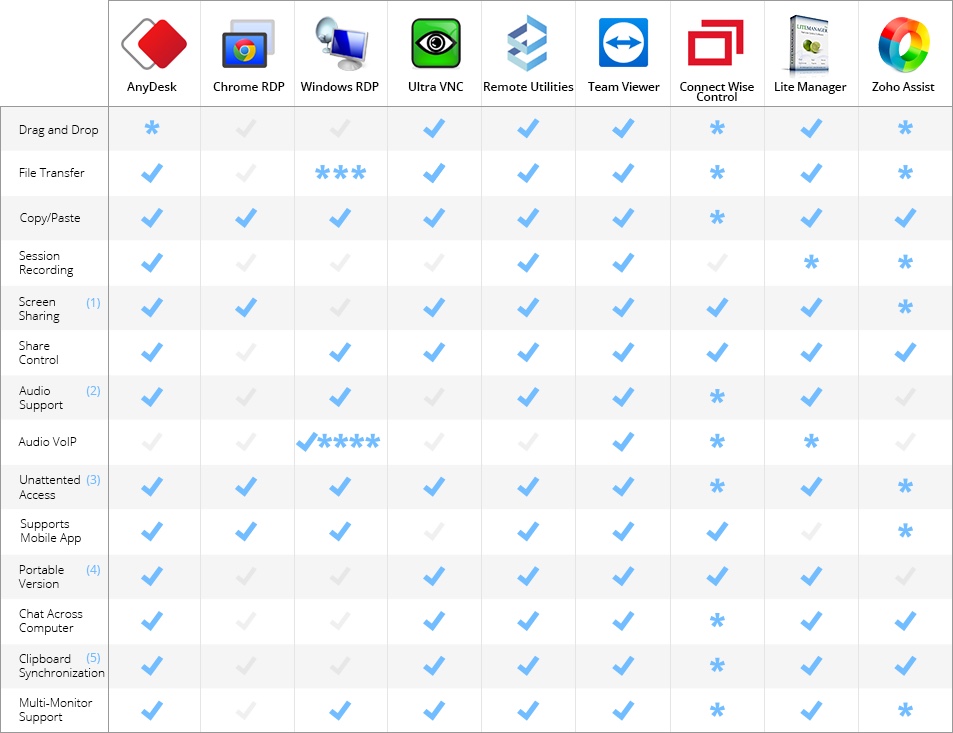
The Dark Side: When RATs Turn Trojan
In cybersecurity jargon, a Remote Access Trojan (RAT) is malware that mimics legitimate remote tools but grants unauthorized, hidden control to attackers. Once installed, a malicious RAT opens a backdoor, allowing hackers to:
- Spy via webcam/microphone
- Log keystrokes and steal credentials
- Capture screenshots
- Download/upload files
- Install additional malware
- Even ransom your data
Unlike viruses that announce themselves with crashes, RATs are stealthy—designed to evade detection while giving attackers full administrative privileges.
Here's a simplified diagram of how a typical RAT operates:

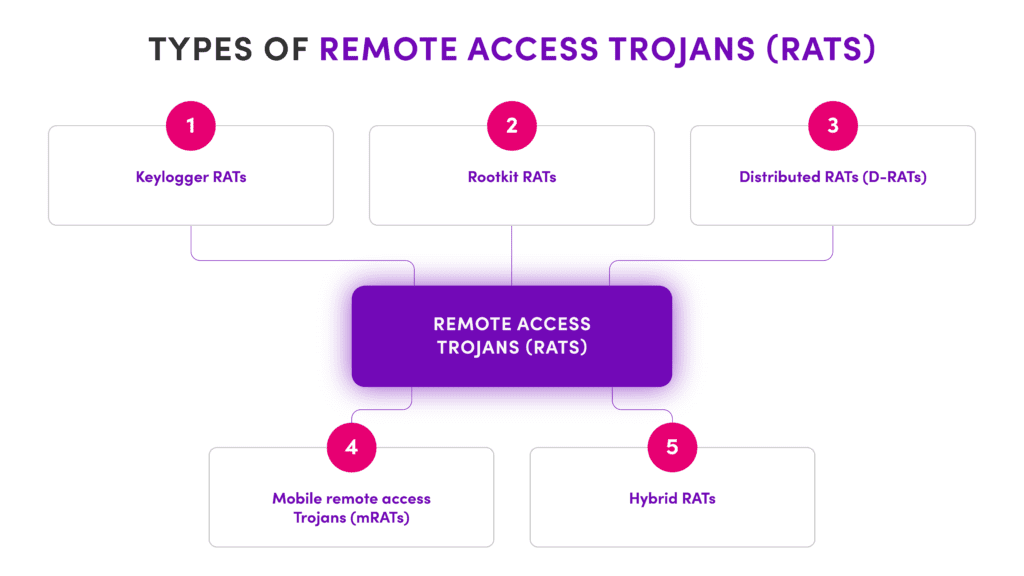
Common infection vectors include phishing emails, malicious downloads, drive-by exploits, or even bundled with cracked software.
Blurring the Lines: Abuse of Legitimate Tools
One of the scariest trends in 2025 is attackers hijacking genuine remote access software. Tools like AnyDesk, TeamViewer, RustDesk, and ConnectWise are frequently abused because:
- They're often whitelisted by antivirus
- Free versions are easy to deploy
- They blend in with normal IT activity
Ransomware gangs and state-sponsored hackers use these for persistence, lateral movement, and data exfiltration. Recent campaigns have targeted logistics firms, financial institutions, and even government networks by tricking users into installing "support" tools that hand over control.
Real-World Threats in 2025
RATs aren't relics—they're evolving. Notable examples include:
- AsyncRAT and Remcos: Commodity RATs sold on the dark web, used for espionage and ransomware deployment.
- GodRAT: A newer threat distributed via Skype, targeting SMBs in the Middle East.
- Mobile RATs like Anubis: Banking trojans with full remote control on Android devices.
In 2024-2025 reports, RATs ranked as the second most common malware sold underground, behind only info-stealers.
How to Defend Yourself and Your Organization
The best defense is layered:
- Patch and Update: Keep software current to close vulnerabilities.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Everywhere, especially on remote access.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Tools that spot anomalous behavior.
- User Education: Never install unsolicited "support" software.
- Zero-Trust Policies: Restrict remote tools to approved ones only, with logging and auditing.
- Network Monitoring: Watch for unusual outbound connections to C2 servers.
Remember: Even legitimate tools can become threats if mismanaged.
Final Thoughts
Remote access tools embody the duality of modern technology—empowering productivity while inviting risk. In cybersecurity, the line between tool and trojan is thinner than ever. Staying informed, vigilant, and proactive isn't just good practice; it's essential survival in our digital age.
Stay safe out there—your next "helpful" remote session might not be from IT support.
Published: December 25, 2025
